Governance, Security & Compliance: A Simple Framework for SMEs
When small businesses hear “compliance,” they often assume it’s complicated and expensive. But cybersecurity compliance for SMEs doesn’t have to be scary. By blending governance, security, and compliance into a cohesive approach, you can strengthen your business without overcomplicating things.
In this post, we explore governance vs. security, why both matter, and how they link into compliance in ways that SMEs can actually manage.
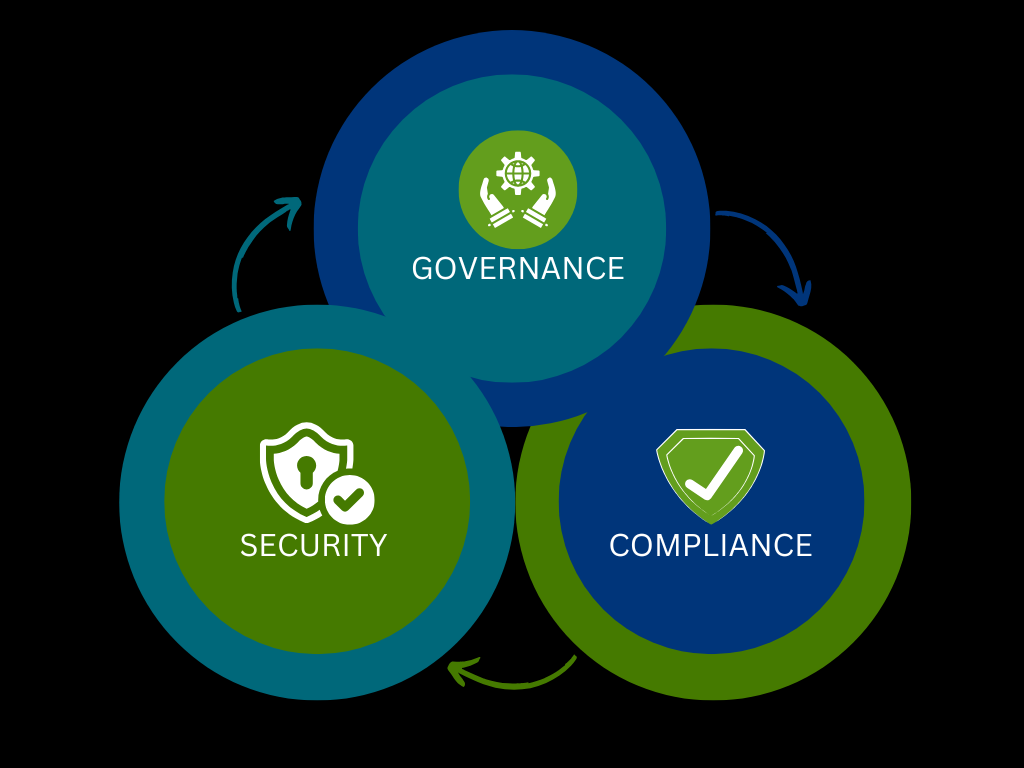
What Is Governance—And How It Differs from Security
First, let’s define these terms clearly:
-
Governance sets the rules, accountability, and structure around cybersecurity decisions. It means deciding who is responsible, how decisions are made, and when policies get reviewed.
-
In contrast, security is about the tools, processes, and controls you deploy—things like firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and incident response.
In short: governance is the oversight; security is the execution. Without governance, security efforts can be inconsistent or misaligned.
Why SMEs Need Both — and How They Support Compliance
Even for smaller organizations, achieving cybersecurity compliance for SMEs means more than checking boxes. Compliance frameworks (GDPR, NIS2, etc.) demand that you can show both governance and security are working together.
-
Governance ensures you have the right roles, policies, and accountability in place.
-
Security ensures those policies are enforced via proper controls, training, and monitoring.
-
Compliance is your proof: audits, reports, and documentation that show you followed those processes.
For more on how SMEs can align governance with rules like NIS2, see this Black Watch post “Cyber Governance for SMEs”.
Thus, governance, security, and compliance form a three-legged stool: lose one, and the whole structure wobbles.
Transitioning from Confusion to Clarity (Steps You Can Take)
To move from uncertainty to practical action:
-
Define Roles & Responsibilities — even if it’s just one person wearing multiple hats.
-
Draft Simple Policies — for access, data handling, incident response. Keep them readable.
-
Implement Key Security Controls — MFA, backups, logging, staff awareness training.
-
Document Everything — who approved what, when reviews happened, how incidents were handled.
-
Review & Adjust — at least annually, or after any security event.
By following these steps, your governance ensures consistency, your security delivers protection, and your compliance shows proof.
Final Thoughts
Many SMEs fear the word “compliance,” but it becomes far more manageable when viewed through the lens of governance and security working together, see more on the topic at Black Watch Security. If you’re ready to move beyond uncertainty and build a sustainable framework, consider starting with a simple policy or role assignment.
For further reading, check out resources from ENISA or the European NIS2 Directive, and explore how Black Watch treats governance, risk, and compliance as foundational in their services.